Fork and Join
Concurrent Programming in Java Plain Old Threads
- 일반적으로 자바에서의 Concurrent programming은 java.lang.Thread와 java.lang.Runnabl를 이용한다
- Dead lock이 발생되지 않도록 하면서 잘못된 read/write가 발생하지 않도록 하기 위해 공유자원을 잘 관리해야한다
-
기본적인 쓰레드 관련 코드는 아래에 있다
Thread thread = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(">>> I am running in a separate thread!"); } }; thread.start(); thread.join();- 메인쓰레드는 join()을 호출하여 생성된 쓰레드가 종료되길 기다리고 있는다
- 다른 쓰레드의 작업이 완료되는 것을 기다리고 있는다
- producer/consumer 패턴은 이와 비슷한 형태를 가지고 있다
- queue에 Task가 가득차 있드면 producer는 queue에 빈 공간이 생길때까지 대기해야한다
- consumer는 queue에 Task가 없다면 대기해야한다
- 동기화하여 Task를 처리하는 것은 Thread-safe 하지만 성능에 문제를 가져온다
- 메인쓰레드는 join()을 호출하여 생성된 쓰레드가 종료되길 기다리고 있는다
Rich Primitives with the java.util.concurrent Packages
-
java.util.concurrent는 Java SE 5에서 처음 소개되었고 Java SE6에서 많은 부분이 개선되었다
import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.*; import static java.util.Arrays.asList; public class Sums { static class Sum implements Callable<Long> { private final long from; private final long to; Sum(long from, long to) { this.from = from; this.to = to; } @Override public Long call() { long acc = 0; for (long i = from; i <= to; i++) { acc = acc + i; } return acc; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); List <Future<Long>> results = executor.invokeAll(asList( new Sum(0, 10), new Sum(100, 1_000), new Sum(10_000, 1_000_000) )); executor.shutdown(); for (Future<Long> result : results) { System.out.println(result.get()); } } }- 2개의 쓰레드를 이용하는 executor를 이용한다
- ExecutorService.invokeAll()는 Callable인스턴스의 Collection을 받으며 그것들의 모든 작업이 처리될때까지 대기한다
- ExecutorService.invokeAll()는 Future 오브젝트들을 리스트 형태로 리턴한다
- Future 객체를 통하여 작업 완료 여부를 알 수 있다
- invokeAll()은 Blocking 메소드이기 때문에 각각의 Future리스트의 Iterator를 돌면서 Sum 결과를 더할 수 있다
- 쓰레드들을 정상적으로 종료시키고 프로그램을 종료시키기 위해서는 shutdown() 메소드는 꼭 호출해야한다
Fork/Join Tasks Overview
- Task를 작은 단위의 SubTask로 나누고 각각의 SubTask를 처리하하여 작업을 완료 시키는 방식
- “divide and conquer”, “map and reduce”와 같은 유형이다
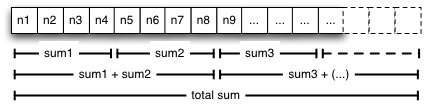
많은 숫자가 들어있는 배열에서 sum을 하는 방법
-
배열은 작은 조각(구간)으로 나누고 각각의 쓰레드에서 구간 별로 sum을 구하고 총 합을 구한다
-
Excecutor를 이용하면 간단하게 만들 수 있다
- 배열은 n개의 조각으로 나눈다
- 각각 부분의 합을 구하기 위한 Callable 인스턴스를 생성한다
- 쓰레드 풀에 있는 쓰레드들에 의하여 각 부분의 sum이 구해진다
- 총 합을 구하기 위해 계산된 각 합을 더한다
나뉘어진 SubTask가 하나의 쓰레드가 처리하기에 충분한가 ?
- 분할된 SubTask의 크기가 쓰레드에서 실행하기에 적당한가 ? 메모리 공간은 충분한가 ?
- SubTask를 더 분할하여 “Divisions” 계층을 생성하고 가장 작은 크기의 Task 부터 처리해야 한다
- 위 기능을 지원하기 위해 Java SE7에서 fork/join framework이 추가 되었다
Additions for Supporting Parallelism
- Java SE7 java.util.concurrent에 fork/join framework이 추가 되었다
- ForkJoinPool Executor는 ForkJoinTask 인터페이스의 인스턴스들을 처리하도록 되어있다
- ForkJoinTask 오브젝트는 SubTask들을 생성 가능 하도록 지원하며 그 SubTask들이 처리 완료 될때까지 대기한다
- Executor의 내부에서는 “stealing” 기법을 이용하여 다른 쓰레드에서 대기 중인 Task들을 가져와서 처리할 수 있도록 되어 있다
- ForkJoinTask에는 2가지 타입이 있다
- RecursiveAction는 리턴 값을 가지지 않는다
- RecursiveTask는 리턴 값을 가지고 있다
Example Code
참고
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/java/fork-join-422606.html
Published 28 March 2016